Microsoft recently advised of a critical TCP/IP Remote Code Execution Vulnerability dubbed CVE 2024-38063, which is a critical unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability within the Windows TCP/IP stack. The flaw can allow attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely on systems with IPv6 (which is enabled by default), without any user interaction. The vulnerability has been assigned a CVSS score of 9.8.
CVE 2024-38063 affects Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server 2008 through 2022.
All versions of Windows that have IPv6 enabled are at risk, which encompasses nearly all modern Windows deployments.
Due to the potential for widespread attacks, immediate action is required. In this blog, we explain what steps are required to protect against this vulnerability and how the Orca Cloud Security Platform can help.
What is CVE 2024-38063?
CVE-2024-38063 arises from an integer underflow issue in the handling of IPv6 packets by the Windows TCP/IP stack. Integer underflow occurs when an arithmetic subtraction results in a value that is smaller than the minimum integer limit. This makes the value unrepresented and knocks the application into an indeterministic state. Hence, improper validation of these packets opens the door for attackers to send specially crafted network requests that exploit the system. This could potentially lead to a complete system compromise with no user interaction required, classifying this CVE as a zero-click vulnerability and a severe security risk.
Potential impact of CVE 2024-38063
If successfully exploited, attackers could gain SYSTEM-level access and thus:
- Execute arbitrary code on the affected system
- Compromisse sensitive data
- Install malware or perform other malicious actions, leading to full system control
Steps to mitigate the vulnerability
Although there is currently no known exploit code, Microsoft tags this vulnerability as likely to be exploited. Because of the severity and criticality of a possible exploitation, this vulnerability requires immediate action.
- Update Windows systems: Administrators should prioritize applying all the relevant Windows patches to protect against this critical vulnerability.
- Disable IPv6 if updating is not possible: For systems where patching is not immediately possible, disabling IPv6 will reduce the attack surface. However, this may disrupt network services that rely on IPv6, so it should be done cautiously. Also, this is only a short-term solution. For long-term protection, the latest security updates should be applied.
- Monitor for anomalous events: Perform ongoing monitoring for unusual IPv6 network traffic.
How the Orca Platform detects and remediates CVE 2024-38063
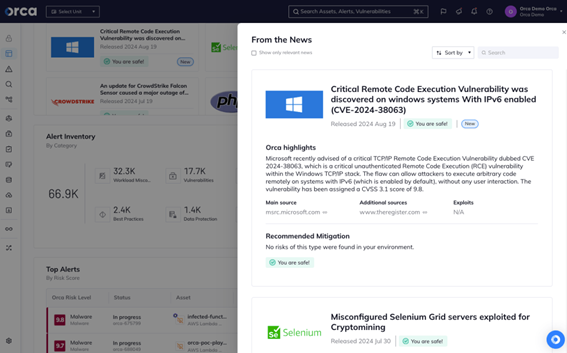
The Orca Security experts list trending vulnerabilities in the ‘From the News’ widget on the Orca Dashboard. Users are automatically shown if their environment is vulnerable to any of these CVEs and how to remediate them.
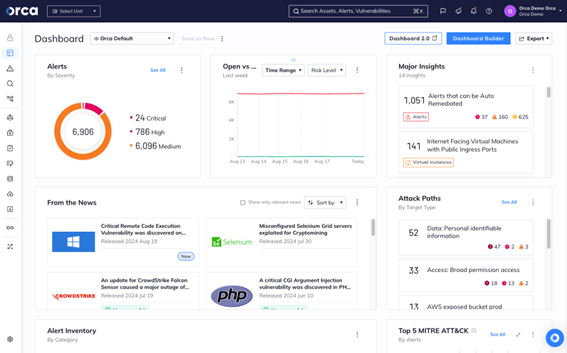
To find out if you are vulnerable to CVE 2024-38063 in your environment, you can click on the news item. This will show all assets with the CVE, allowing you to drill down further and get details on each specific asset.
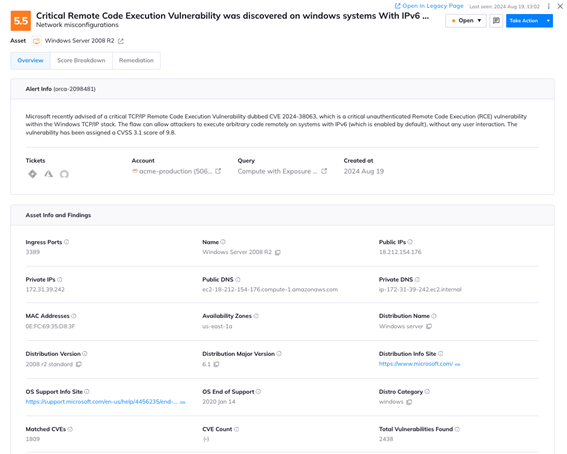
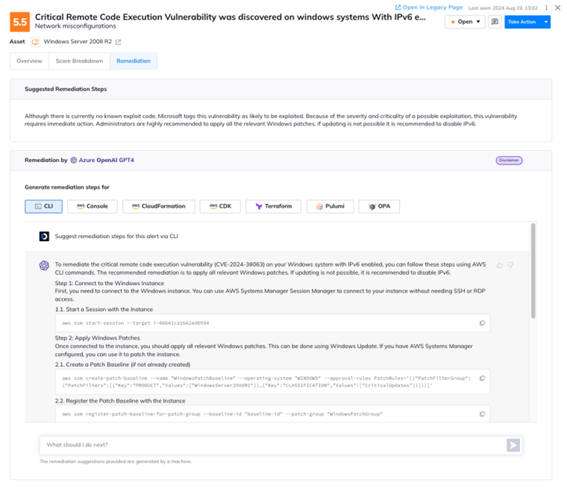
Remediating CVE 2024-38063
Orca includes remediation instructions for each alert, and also includes built-in generative AI to allow you to generate remediation code and steps for the console, CLI, and IaC tools such as Pulumi and Terraform, helping you dramatically speed up mean time to resolution (MTTR).
Orca also integrates with Jira and ServiceNow, allowing you to assign tickets for remediation, and optionally include the AI generated remediation instructions.
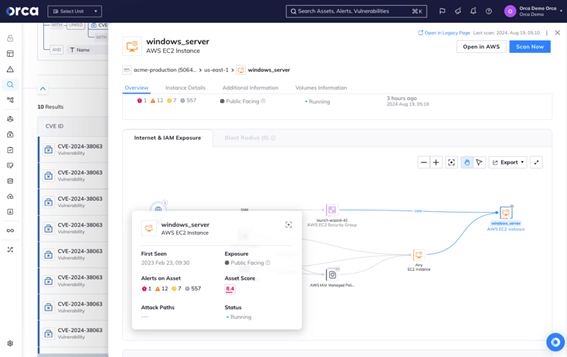
Prioritizing CVE 2024-38063
To ensure cloud security professionals optimize their time and don’t get overwhelmed by low priority alerts, Orca doesn’t only report on the presence of each CVE 2024-38063, but also determines which vulnerabilities should be tackled first.
Using its deep contextual insights, Orca automatically scores the criticality of each vulnerability by considering several factors, including exposure of the vulnerability to the internet and potential business impact if the asset was compromised. Is there sensitive data on the asset? Are there other risks on the asset that would create a direct path to the organization’s most critical business assets?
By looking at the entire context, Orca can instantly show which risks pose the greatest risk and therefore should be remediated first.
Artigo traduzido e disponibilizado pela DigitalSkills Consulting - Distribuidora oficial de soluções de cibersegurança do fabricante Orca Security. Para mais informações: www.digitalskills.pt | [email protected] | 21 418 05 21
Artigo original no site do fabricante em https://orca.security/resources/blog/mitigate-cve-2024-38063-critical-rce-vulnerability-windows-ipv6/